I was downloading some stuff on one machine, and noticed that my Ethernet connection had a very high throughput – but it was doing nothing useful. This blog post gives some of the things I did to identify and resolve the problem.
Mount the file system
I used the command
sshfs colin@10.1.0.3:/home/zPDT/ ~/mountpoint
to mount the file system from 10.1.03 on my local machine.
Identify the problem
I used the Linux command nload to show the network activity.
For my wireless link (downloading a big file) the output was
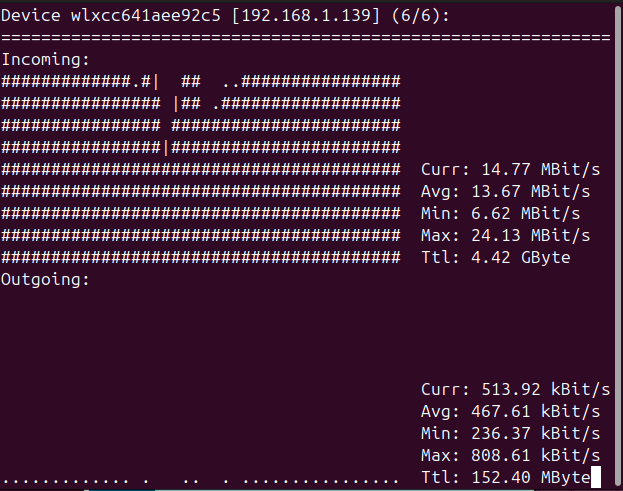
I cannot currently reproduce the sustained Ethernet usage problem.
Wireshark showed my a lot of activity for SSH from port 55401 to port 22.
If you do not have access to Wireshark, the following command show all the socket activity which may help.
ss -t -a -i -O |grep delivery|awk '{print $4,$5, " ", $30,$31 }'
To find the owner of port 55401 I used the show socket command
ss -p |grep 55104
tcp ESTAB 0 0 10.1.0.2:55104 10.1.0.3:ssh users:(("ssh",pid=7258,fd=3))
This gave me the process id of the owner of the port. The ps command gives more information
ps -ef |grep 7258
colinpa+ 7258 ... ssh -x -a -oClearAllForwardings=yes -2 colin@10.1.0.3 -s sftp
Showing the sftp to 10.1.0.3.
How to stop the sftp?
The documentation for sshfs says use the fusermount3 command.
$fusermount3 -u ~/mountpoint
fusermount3: failed to unmount /home/colinpaice/mountpoint: Device or resource busy
I needed to use the lazy unmount option -z
fusermount3 -z -u ~/mountpoint
and this successfully unmounted the remote file system
Chaff
I found out that information can be obtained from the profile of key strokes, and so chaff has been added to the SSH flow.
I fixed it by using setting ObscureKeystrokeTiming no in /etc/ssh/ssh_config. The documentation says
Specifies whether ssh(1) should try to obscure inter-keystroke timings from passive observers of network traffic. If enabled, then for interactive sessions, ssh(1) will send keystrokes at fixed intervals of a few tens of milliseconds and will send fake keystroke packets for some time after typing ceases. The argument to this keyword must be
yes,noor an interval specifier of the forminterval:milliseconds(e.g.interval:80for 80 milliseconds). The default is to obscure keystrokes using a 20ms packet interval. Note that smaller intervals will result in higher fake keystroke packet rates.